power brakes vs manual
Power Brakes vs. Manual Brakes⁚ A Comprehensive Guide
This comprehensive guide delves into the world of power brakes and manual brakes, exploring their fundamental differences, advantages, disadvantages, and performance considerations. We’ll also discuss conversion and installation aspects, helping you choose the right braking system for your vehicle.
Introduction
The choice between power brakes and manual brakes is a crucial one for any car enthusiast or owner. While both systems aim to bring your vehicle to a safe stop, their underlying mechanisms and performance characteristics differ significantly. Power brakes, as the name suggests, utilize engine vacuum to assist in applying brake force, making it easier for the driver to stop the car. Manual brakes, on the other hand, rely solely on the driver’s physical input to create the necessary pressure to engage the brakes. This guide explores the intricacies of both systems, shedding light on their respective advantages and disadvantages, and helping you determine the best fit for your driving needs and vehicle.
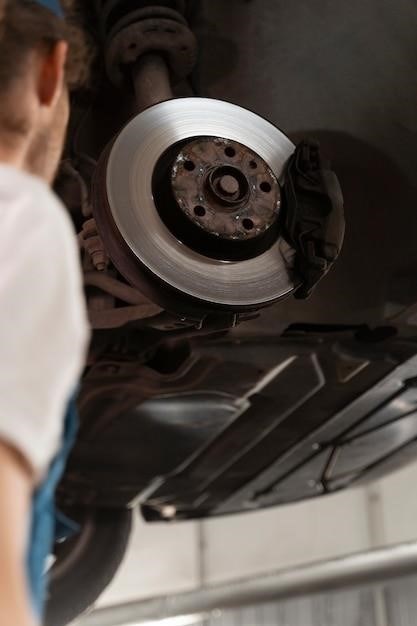

The Fundamentals of Power Brakes
Power brakes leverage the power of your engine to enhance braking performance. When you press the brake pedal, a vacuum booster, connected to the engine’s intake manifold, creates a partial vacuum. This vacuum pulls on a diaphragm inside the booster, multiplying the force you apply to the pedal. The increased force is then transmitted to the master cylinder, which in turn pushes brake fluid to the calipers or wheel cylinders, effectively engaging the brakes. This power assistance significantly reduces the effort required to stop the vehicle, resulting in quicker and more efficient braking, especially in emergency situations.
Understanding Manual Brakes
Manual brakes rely solely on the physical force applied to the brake pedal to activate the braking system. When you press the brake pedal, the force is directly transferred to the master cylinder, which then pushes brake fluid to the calipers or wheel cylinders. The brake fluid pressure then activates the brake pads or shoes, creating friction against the brake rotors or drums, slowing the vehicle down; This system provides a more direct connection between the driver and the brakes, offering a higher level of feedback and control, particularly for experienced drivers. While manual brakes are less demanding in terms of maintenance compared to power brakes, they require more physical effort to operate, especially during high-speed driving or emergency braking.
The Key Difference⁚ Power Boosters
The fundamental distinction between power brakes and manual brakes lies in the presence of a power booster. This crucial component utilizes engine vacuum to amplify the force applied to the brake pedal, making it easier to stop the vehicle. When you press the brake pedal, the vacuum in the booster assists in pushing the master cylinder piston, generating increased pressure for the brake fluid. This results in a more efficient braking system, requiring less physical effort from the driver. While power brakes significantly enhance stopping power and reduce driver fatigue, they introduce a layer of complexity to the braking system, requiring more components and potential maintenance. However, the added convenience and improved braking performance make them the preferred choice for most modern vehicles.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Power Brakes
Power brakes offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for modern vehicles. The most significant benefit is their increased stopping power, allowing for faster and more efficient braking, particularly in emergency situations. This enhanced braking capability results in shorter stopping distances, improving overall safety. Additionally, power brakes significantly reduce driver fatigue, as less physical effort is required to apply the brakes. This is especially beneficial during long drives or in heavy traffic. However, power brakes also come with certain disadvantages. They are more expensive than manual brakes due to the additional components required, and they require more maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Furthermore, power brakes can be susceptible to malfunctions, particularly if the vacuum system is compromised. While these drawbacks exist, the benefits of power brakes generally outweigh the disadvantages, making them a worthwhile investment for most drivers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Manual Brakes
Manual brakes offer a simpler and more direct braking experience, with advantages that appeal to some drivers. Their primary advantage lies in their simplicity, making them less prone to malfunctions and easier to maintain. The absence of a power booster translates to a more direct connection between the driver’s foot and the braking system, providing a greater sense of control and feedback. This is particularly appreciated by enthusiasts who prioritize precise control and feel, especially in performance driving situations. However, manual brakes also come with certain disadvantages. They require significantly more physical effort to apply, which can lead to fatigue, particularly during long drives or in heavy traffic. Furthermore, manual brakes offer less stopping power compared to power brakes, resulting in longer stopping distances. This reduced stopping power can pose a safety concern in emergency situations, as it might not provide sufficient braking force to prevent an accident.
Performance Considerations
The choice between power and manual brakes often boils down to performance considerations. Power brakes offer quicker and more efficient stopping, especially in emergency situations, due to their ability to amplify braking force. This is particularly beneficial in heavier vehicles or when hauling heavy loads. However, some drivers find that the added assistance of power brakes can lead to a less precise and less “connected” feel, especially in situations where fine control is critical. In contrast, manual brakes provide a more direct feel and greater feedback, allowing for more precise braking modulation, which is highly prized in performance driving and racing applications. The direct connection between the driver’s foot and the brakes allows for a more nuanced and deliberate braking response, enabling drivers to better control the vehicle’s deceleration. Ultimately, the optimal choice depends on your individual needs and driving preferences. If you prioritize stopping power and ease of use, power brakes are the better option. If you desire precise control and feedback, manual brakes might be more suitable.
Conversion and Installation
Converting from power brakes to manual brakes, or vice versa, involves a few key steps. A power brake conversion generally involves replacing the master cylinder with a manual one, removing the power booster, and potentially modifying the brake lines. This can be a relatively straightforward process, particularly if you’re working with a vehicle that was originally equipped with manual brakes; A manual brake conversion to power brakes, on the other hand, requires installing a new master cylinder designed for power brakes, adding a power booster, and potentially adjusting the brake pedal linkage. The process can be more complex, requiring careful attention to the brake system’s hydraulics and the integration of the power booster. While both conversions are feasible, it’s crucial to consider the specific requirements of your vehicle and the potential need for adjustments to the brake pedal linkage, master cylinder size, and brake line routing. It’s also essential to ensure proper bleeding of the brake system after any conversion to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Choosing the Right System for Your Vehicle
Selecting the right braking system for your vehicle involves considering various factors. For classic car restorations, manual brakes might be preferred for authenticity, especially if you plan to use the vehicle for vintage events or shows. If you prioritize enhanced stopping power and ease of use, power brakes are the way to go, offering a more comfortable driving experience. However, remember that power brakes come with the added complexity of a booster and require regular maintenance to ensure proper operation. If your vehicle is designed for spirited driving, such as racing or track events, manual brakes might be a better choice, providing precise feedback and control. Ultimately, the decision comes down to your driving style, vehicle application, and personal preferences. Consider your budget, the complexity of installation, and the potential need for future maintenance when weighing your options.
The choice between power brakes and manual brakes hinges on your individual needs and priorities. While power brakes offer enhanced stopping power and ease of use, they come with the added complexity of a booster and require regular maintenance. Manual brakes, on the other hand, provide precise feedback and are simpler to maintain but demand more physical effort. When making your decision, weigh the factors of performance, feel, budget, maintenance, and the intended application of your vehicle. Consider if you prioritize ease of use or precise control, and remember that both systems have their merits. Ultimately, the best braking system is the one that best suits your driving style and the specific requirements of your vehicle.
FAQs
Q⁚ Why would I convert from power brakes to manual brakes?
A⁚ There are situations where vacuum-assisted power brakes might cause problems, such as insufficient vacuum in high-performance engines or when racing. Converting to manual brakes can solve these issues and offer a more responsive feel, particularly for competitive driving.
Q⁚ How do I know if my brakes are manual or power?
A⁚ The key difference is the presence of a power brake booster. If you see a round, metal cylinder attached to the master cylinder, you have power brakes. If you don’t see this cylinder, you have manual brakes.
Q⁚ Can I convert my manual drum brakes to power drum brakes?
A⁚ Yes, you can convert from manual drum brakes to power drum brakes. It involves replacing the master cylinder with a power-assisted one and installing a power brake booster. However, remember that the entire brake system needs to be compatible with the power setup.